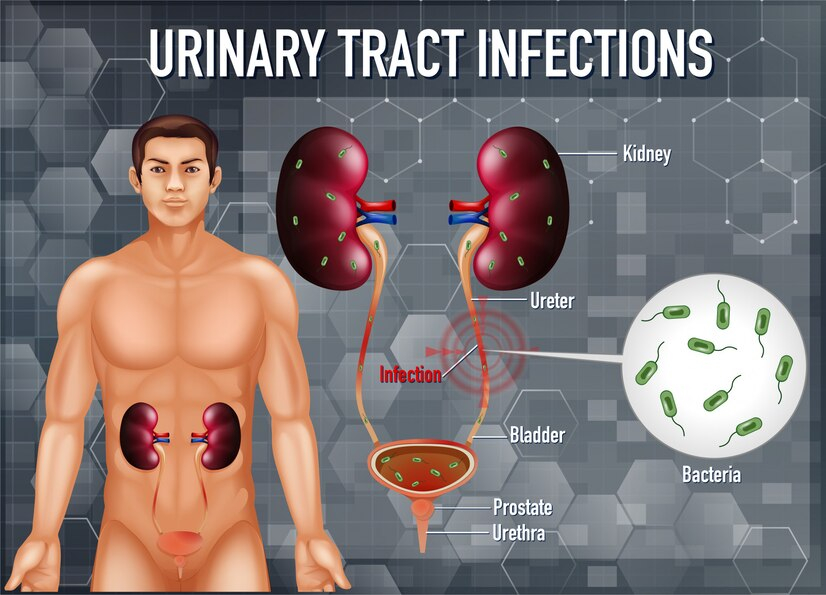
Urinary tract infection is a common infection these days, it can affect any part of the urinary system like kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra. It can affect both men and women but it is more common complication found in women. This infection starts at the lower urinary tract (urethra and bladder) which is painful and irritating but in some cases, infection can reach up to kidney i.e. serious health threat.
Bacteria - E. coli is the most common cause of the urinary tract infection. Urine is the byproduct of blood filtration by the kidney. Kidneys filter the blood and separate the waste material and extra water from your blood, this process generates urine. Urine is usually passed down in urinary bladder without any contamination. Sometimes bacteria can enter your urinary system, which results in urinary tract infections.
Urinary system: parts & its functioning -
Kidneys - Kidneys are small beans like structure located in both side on back of your body above hips. It filters blood and separate the waste material like urea and creatinine from blood, mix it with extra water in the blood and generate urine.
Ureters - Both kidneys are connected with bladder through a tubelike structure called ureter, which passes the urine from kidneys and dumped it into bladder for release.
Bladder - Bladder is a balloon like stretchable organ that stores urine before releasing it out of your body.
Urethra - Urethra is last part of urinary system, it is an exit point that carries the urine from bladder to the outside of your body.
Cause, signs and symptoms:
Early signs of UTIs -
Urinary tract infection causes the inflammation of the lining of urinary tract especially in urethra and bladder. The inflammation can lead to the following discomfort:
• Pain in the pelvis, abdomen and lower back
• Pressure the lower part of pelvis
• Foul smell coming from urine
• Dysuria (pain during urination)
• Hematuria (presence of blood in your urine)
• Frequent urination
There are some other symptoms involved like -
• Pain in penis
• Fatigue
• Fever
• Chills
• Vomiting
• Nausea
Cause of UTIs -
Microorganisms like bacteria can enter your urinary system through natural opening of urethra and can cause infection in bladder. In serious conditions, if infection is not detected it can reach up to ureter and infect kidney as well. Personal hygiene of penis and opening of vagina is important, precautionary measures are important as it can easily be transmitted through an infected partner.
E. coli is the most common bacteria that causes UTIs, it is responsible for more than 90% of UTIs. E. coli is usually found in the larger intestine.
Mostly affected people of UTIs -
Anyone can get a urinary tract infection but females are more likely to get UTIs, this is because of smaller urethra than men and urethra is closer to anus where presence of E. coli is common or UTIs can be result of improper handling of menstrual hygiene.
Bacteria can also enter into urethra through your fingers. You can introduce bacteria to urethra during sexual activity or when you go to the bathroom. Wash your hands before and after having sex or going to the bathroom.
Diagnosis and tests:
After having the above discussed symptoms your healthcare provider may ask you to get one of the following tests to detect the urinary tract infection-
• Urinalysis - In this test, lab technicians collect the urine sample and perform the tests to detect the signs of infections, using variables like nitrites, leukocyte esterase and white blood cells.
• Urine culture - Urine is collected in a cup and test will be performed to grow or detect the presence of any bacteria in the collected urine. It is important diagnosis method as it helps your healthcare team to plan right treatment.
If infection do not respond to the early treatments and shows no improvement then your healthcare provider may ask for the following tests -
• Ultrasound - Ultrasound is effective non-invasive imaging test which doesn’t require much of preparation. It gives a better look of the organs and part of urinary system.
• CT scan - CT scan is another imaging test. It is a type X-rays that creates the 3D images of internal organs. It is more precise than the normal X-ray images.
• Cystoscopy - In this test, a cystoscope is used to look at the internal lining of your urethra and bladder. It is an instrument with a tube with lens and a light at one end which enters through the natural opening of urethra into bladder or ureter if needed to look at inner lining of bladder or any damage caused by infection.
Management and treatment -
After the detection of infection doctors usually look at the cause of infection and bacteria, which helps them plan the right treatment and medication for you. You need antibiotics to treat a UTI. doctor will prescribe the right antibiotic for you that will work best for you. It is important to complete the course of the treatment. Do not stop taking medicine on your own, the infection may return and make it more challenging to treat.
Intravenous (IV) treatment - This a treatment plan for complicated cases in which infection reaches the kidneys and oral antibiotics are not responding well in such cases, your provider will inject medicines in your arm (intravenously).